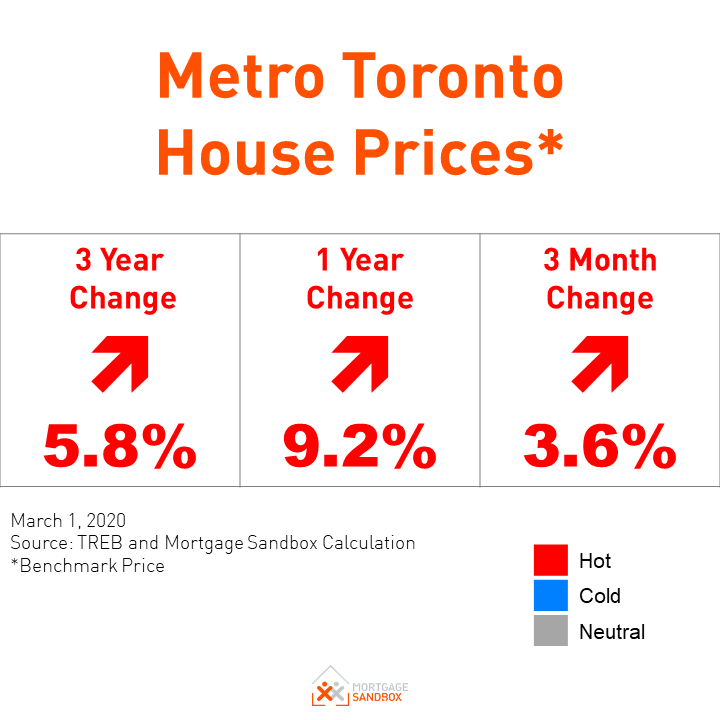
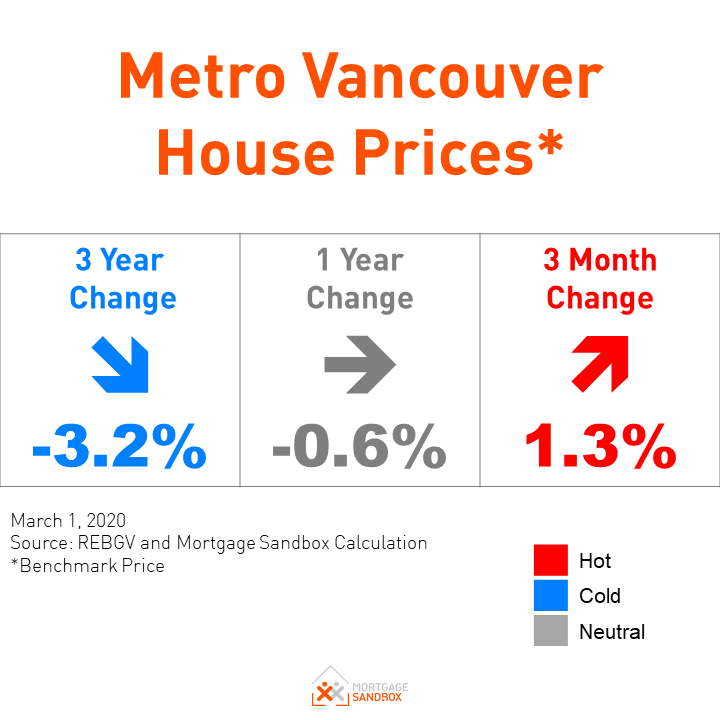
What is the Prime Rate in Canada?
Prime Rate
The prime rate in Canada is currently 3.95%. The prime rate, otherwise known as the prime lending rate, is the annual interest rate Canada’s major banks and financial institutions use to set interest rates for variable loans and lines of credit, including variable-rate mortgages.
The prime rate is primarily influenced by the policy interest rate set by the Bank of Canada (BoC), also known as the BoC's target for the overnight rate (The target rate).
Find out what’s happening with rates this year by checking out our
Canada Interest Rate Forecast
What is the prime rate?
When you apply for a loan with a variable interest rate, your lender will give you an annual interest rate that’s tied to the bank’s prime rate. All kinds of loans are based on this rate, including certain mortgages, car loans, personal lines of credit, and even some credit cards. Think of the prime rate as the anchor these other interest rates are based on. As the prime rate moves around, so too does the amount of interest you pay on your loans.
How is the prime rate set?
Each bank sets its own prime rate, but the big five banks usually all have the same prime rate. As we already mentioned, the prime rate is predominantly influenced by the BoC's target for the overnight rate. When the BoC raises the overnight rate, it becomes more expensive for banks to borrow money, and they raise their respective prime rates to cover the added costs. Conversely, when the BoC lowers the overnight rate, banks usually lower their prime rates by the same amount.
This chart shows the relationship between the overnight rate and the prime rate over time. As you can see, the rates usually move in lockstep, but not always. In recent years, there have been times when the BoC has lowered the overnight rate, but the banks have not passed on the full discount to their customers.
Prime vs Overnight Rate From 2000 - Today
Mortgage Renewal?
Find a mortgage broker who shares your priorities and specializes in your local area.
How does the prime rate affect mortgage rates?
There are two main types of mortgage rates in Canada – fixed and variable. When you get a fixed mortgage rate, you agree to pay the same rate over the entire course of your mortgage term regardless of what happens in the outside market. Fixed mortgages are a good option if you’re worried mortgage rates will go up, or if you want to enjoy the stability of paying the same mortgage rate until it’s time to renew.
When you get a variable mortgage rate, the rate will be expressed as the prime rate plus or minus a certain percentage. When the prime rate goes up or down, your mortgage rate will go up or down by the same amount. Variable mortgages usually come with a lower rate vs. fixed-rate mortgages when you sign up, but there’s the risk that the rate could go up (or down) during your mortgage term. Many lenders will allow you to convert a variable-rate mortgage to a fixed-rate mortgage at any time, but you will have to pay the fixed rate as of the time you decide to switch.
Historical prime lending rates
This chart shows the prime rate over time, starting in 1935. The prime rate has moved massively over time, ranging from historic highs around 23% in the early 1980s to historic lows of 2.25% following the great recession.